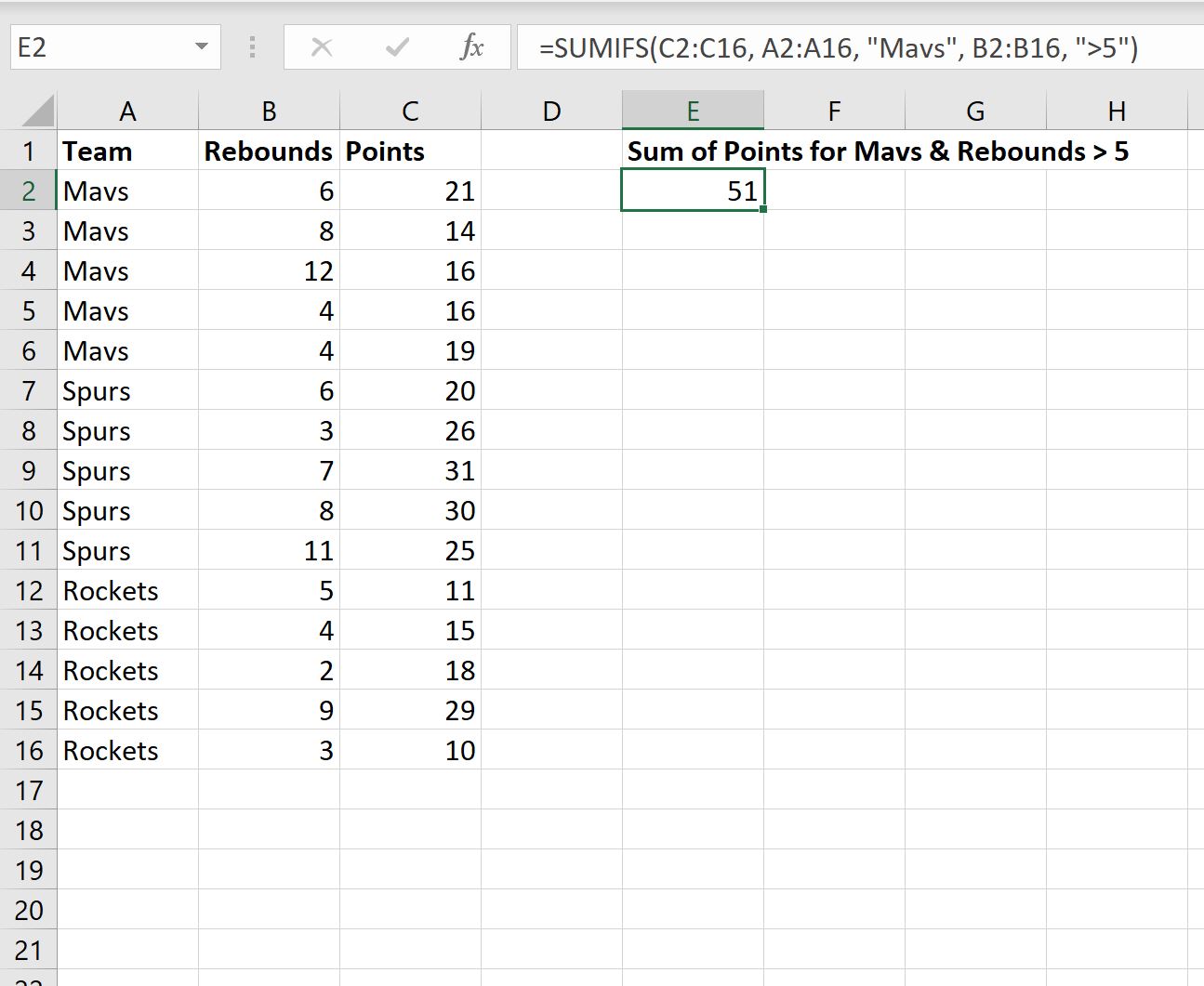
The SUMIF function in Excel returns the sum of cells that meet a single condition, while the SUMIFS function returns the sum of cells that meet multiple criteria.
The syntax for SUMIF is:
=SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range])
Where range is the range of cells to apply the criteria to, criteria is the condition that cells must meet, and sum_range is the range of cells to sum. If sum_range is not provided, SUMIF will sum the cells in the range argument instead.
The syntax for SUMIFS is:
=SUMIFS(sum_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], …)
Where sum_range is the range of cells to sum, criteria_range1 is the range of cells to apply the first condition to, criteria1 is the first condition, and additional criteria ranges and conditions are optional.
Here are some examples of how to use SUMIF and SUMIFS:
-
To sum all numbers in a range that are greater than 5:
=SUMIF(range, “>5”)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, “>5”)
-
To sum all numbers in a range that are equal to a value in another cell:
=SUMIF(range, criteria_cell)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, criteria_cell)
-
To sum all numbers in a range that are not equal to a value:
=SUMIF(range, “<>value”)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, “<>value”)
-
To sum all numbers in a range that are between two values:
=SUMIF(range, “>min_value”) + SUMIF(range, “<=max_value”)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, “>min_value”, range, “<=max_value”)
-
To sum all numbers in a range that contain a specific text string:
=SUMIF(range, “text“)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, “text“)
-
To sum all numbers in a range that do not contain a specific text string:
=SUMIF(range, “<>text“)
=SUMIFS(sum_range, range, “<>text“)
As you can see, SUMIFS is more versatile than SUMIF because it can apply multiple conditions to a range of cells. However, SUMIF is simpler to use and may be more appropriate for certain situations.
Here are some tips for using SUMIF and SUMIFS:
- The criteria argument in SUMIF can be a text string, a number, a cell reference, a logical test, or a function that returns a logical value.
- The criteria range and sum range arguments in SUMIF must have the same size and shape.
- The criteria argument in SUMIF can use wildcards (*, ?) for partial matching.
- The criteria argument in SUMIF can use logical operators (>, <, <>, =) to specify a condition.
- The criteria argument in SUMIF can use the ampersand (&) to concatenate values or cell references.
- The criteria argument in SUMIF can use the tilde (~) to escape a literal wildcard character.
- The criteria range and sum range arguments in SUMIFS must have the same size, but the criteria ranges can have a different size.
- The criteria arguments in SUMIFS can use logical operators (>, <, <>, =) to specify a condition.
- The criteria arguments in SUMIFS can use the ampersand (&) to concatenate values or cell references.
- The criteria arguments in SUMIFS can use the tilde (~) to escape a literal wildcard character.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.