A Python list and a tuple are both ordered collections of items.
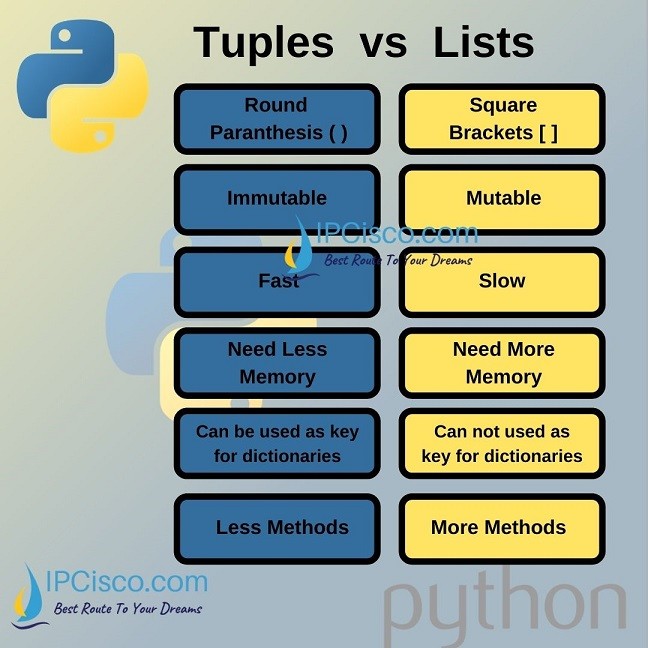
Mutability:
Lists are mutable, which means their content can be changed after they are created. This allows you to add, remove, or modify elements within a list.
Tuples, on the other hand, are immutable. Meanwhile and once a tuple is created, its content cannot be changed. Therefore, you cannot add, remove, or modify elements within a tuple.
Syntax:
Lists are created using square brackets [], and their elements are separated by commas. For example: my_list = [1, 2, 3].
Tuples are created using parentheses (), and their elements are also separated by commas. For example: my_tuple = (1, 2, 3and 4).
Use Cases:
Lists are commonly used when you need a collection of items that can be changed after it is created.
Tuples are used when you need a collection of items that should not be changed after it is created. This makes tuples more suitable for heterogeneous (different) datatypes, while lists are more suitable for homogeneous (similar) datatypes.
Memory:
Since lists are mutable, they can use more memory because they need to be able to handle changes in size. Tuples, being immutable, use less memory because they do not need to be able to handle changes in size.
In summary, the choice between a list and a tuple depends on the specific requirements of your code. Use a list when you need a collection of items that can be changed, and use a tuple when you need a collection of items that should not be changed.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.