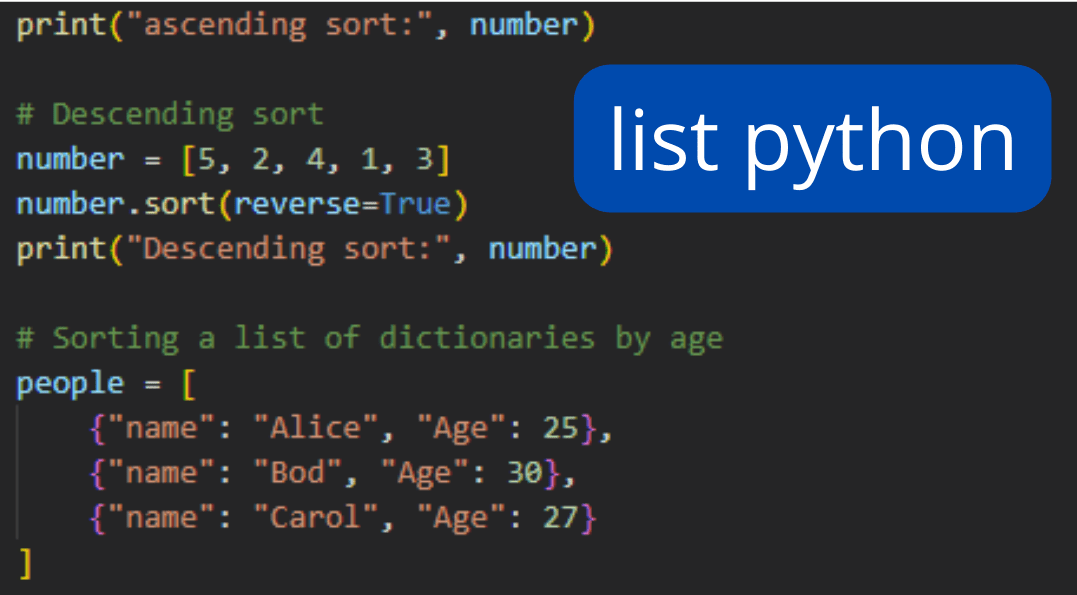
In Python, a list is what we refer to as a collection of items. It is one of the four built-in data types, along with integers, strings, and Boolean values. Lists can be used to store any number of items, and they can be of mixed data types, meaning that a list can contain both integers and strings, for example.
Lists in Python are ordered and changeable, meaning that items in a list can be rearranged and modified. Lists can also contain other lists, making them capable of storing complex data structures.
Here’s an example of a list in Python:
1 fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']In this example, fruits is a list containing three strings.
To access the elements of a list, you can use their index, which starts from 0. For example, fruits[0] would give you the first element of the list, ‘apple’.
Lists in Python can also be manipulated using various built-in methods and operators. For example, to add an element to the end of a list, you can use the append() method:
1 fruits.append('orange')This would add ‘orange’ to the end of the fruits list.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.