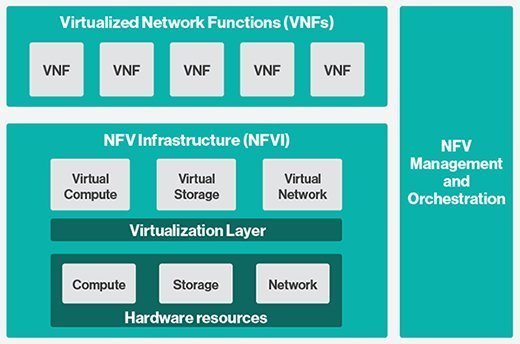
Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) are network services that were previously executed by proprietary, dedicated hardware technology but are now executed on open computing platforms through virtualization.
They allow for the migration of individual network and network security tasks from specialized hardware devices to software that operates on commodity hardware. VNFs can be deployed more quickly and efficiently than traditional networks, improving the scalability and agility of a network while also allowing for more efficient use of infrastructure resources.
They can run inside virtual machines (VMs) or containers on standard virtualization infrastructure software. VNFs are essential for enterprises designing next-generation service architectures and offer a platform for providing secure, flexible services at a lower cost and with more flexibility than traditional monolithic hardware-centric legacy systems.
They can be interconnected like building blocks through service chaining, which is streamlined and offers significant scalability in comparison to traditional network architectures.
How to configure VNF
Configuring Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) involves several steps, which can vary based on the specific VNF and the virtualization infrastructure software being used.
Steps:
-
Select and Obtain the VNF: The first step is to select the specific VNF that meets the requirements of the network service to be provided. Once selected, the VNF software package must be obtained from the vendor or developer.
-
Install and Configure Virtualization Infrastructure Software: VNFs run on virtualized infrastructure, so it’s necessary to have virtualization infrastructure software (such as a hypervisor) installed and configured on the physical server or servers.
-
Deploy the VNF: Once the virtualization infrastructure is in place, the VNF software package can be deployed as a virtual machine (VM) or container. The VNF vendor or developer will provide instructions on how to deploy the VNF.
-
Configure the VNF: After deployment, the VNF must be configured to provide the desired network service. This typically involves configuring network interfaces, routing tables, firewall rules, and other network parameters. The specific configuration steps will depend on the VNF and the network service being provided.
-
Test the VNF: After configuration, it’s important to test the VNF to ensure that it is functioning correctly and providing the desired network service. Testing should include both functional and performance testing to ensure that the VNF meets the desired requirements.
-
Orchestrate and Manage the VNF: Once the VNF is deployed, configured, and tested, it must be managed and orchestrated as part of the overall network architecture. This typically involves using a network orchestration and management system to manage the lifecycle of the VNF, including scaling up or down as needed, and handling faults and failures.
-
Monitor and Maintain the VNF: Finally, it’s important to monitor and maintain the VNF to ensure that it continues to provide the desired network service. This includes monitoring performance metrics, handling failures, and performing regular maintenance tasks such as software updates and patches.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.