-
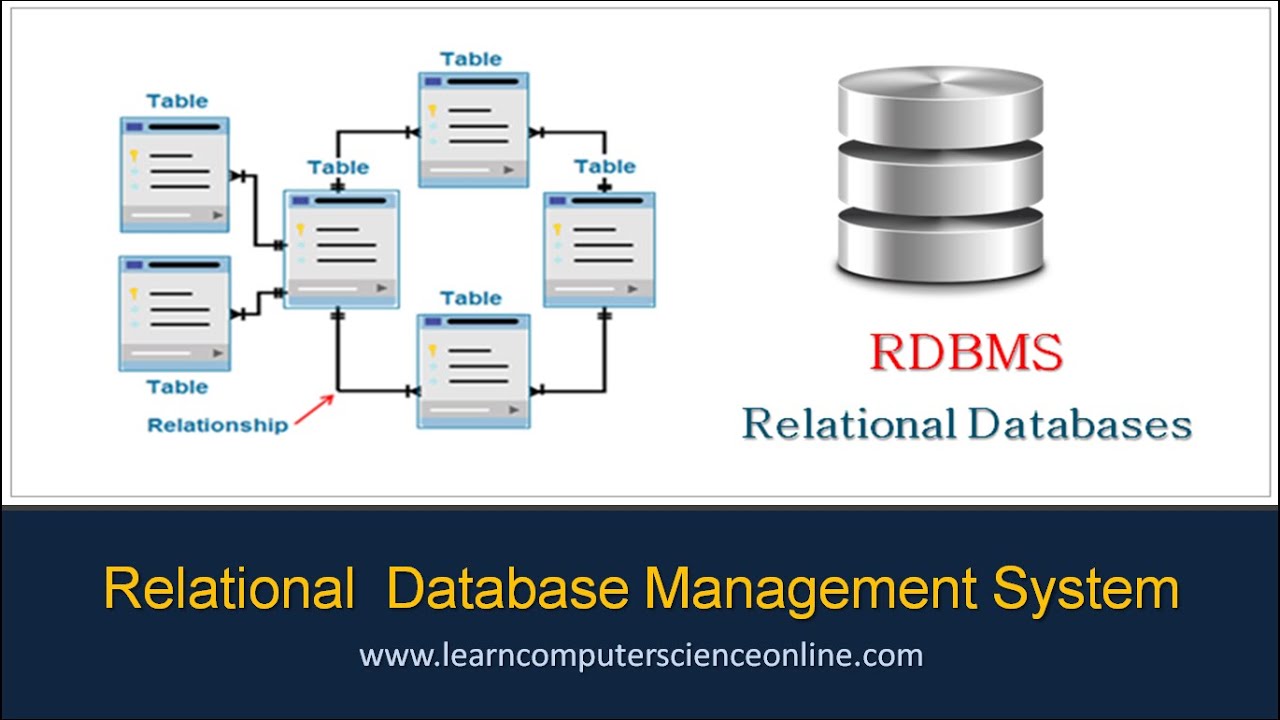
Database: A collection of structured data, typically stored electronically in a computer system.
-
Field (Column): A column in a table that holds a particular type of data, such as a text string or a number. Each field in a table has a unique name.
-
Record (Row): A single row in a table, consisting of a related group of fields (columns).
-
Primary Key: A unique identifier for a record in a table. A primary key must contain a unique value for each record and cannot be null.
-
Foreign Key: A field or collection of fields in a table that is used to refer to the primary key of another table.
-
Index: A performance-tuning method used to speed up data retrieval.
-
Join: A way to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them.
-
SQL (Structured Query Language): A programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
-
Normalization: A systematic approach of decomposing tables to eliminate data redundancy and improve data integrity.
-
Schema: The structure of a database, including all its tables, fields, and relationships.
-
CRUD: The basic operations that can be performed on a database: Create, Read, Update, and Delete.
-
Integrity Constraint: A rule that must be enforced on a database table to maintain data consistency and integrity.
-
ACID Properties: A set of properties that guarantee reliable and consistent transaction execution. These characteristics include durability, isolation, consistency, and atomicity.
-
Transaction: A single unit of work performed by a database management system, which can include multiple operations (e.g., inserting, updating, or deleting records).
-
Concurrency Control: A technique used by a database management system to manage simultaneous transactions and ensure data consistency and integrity.
-
View: A virtual table based on the result-set of a query.
-
Stored Procedure: A set of SQL statements stored in a database, which can be executed as a single unit.
-
Trigger: A special kind of stored procedure that automatically executes (or “fires”) in response to a specific event, such as the insertion or deletion of a record.
-
Function: A set of SQL statements that can be called within a SQL statement and can return a value.
-
Operating System: A software system that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides various services for computer programs.
-
User: An individual who uses a database system.
-
Owner: A database user who has administrative privileges for a particular database object, such as a table or a view.
-
User Role: A group of database users that share the same set of privileges.
-
Server: A computer program that provides resources and services to other programs, such as database clients, over a network.
-
Client: A computer program that accesses the resources and services provided by a server over a network.
-
Backup: A copy of a database, usually created to ensure data integrity and security in case of system failures.
-
Recovery: The process of restoring a database to a consistent state after a system failure.
-
Restore: The process of replacing a database with a backup copy, usually done to recover from a system failure.
-
Admin: A user who has administrative privileges to manage and configure a database system.
-
Script: A sequence of SQL statements or commands that can be executed to perform a specific task.
-
Module: A software component that provides a specific function or feature within a database system.
-
Database Engine: The core component of a database system responsible for processing SQL commands and managing the database files.
-
Driver: A software component that allows a client program to interact with a database system through a specific interface or protocol.
-
Connector: A software component that allows a client program to connect to a database system.
-
Blob (Binary Large Object): A type of field that can store large binary data, such as images or documents.
Note:
In the upcoming database management system tour, numerous additional terminologies will be covered.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.