-
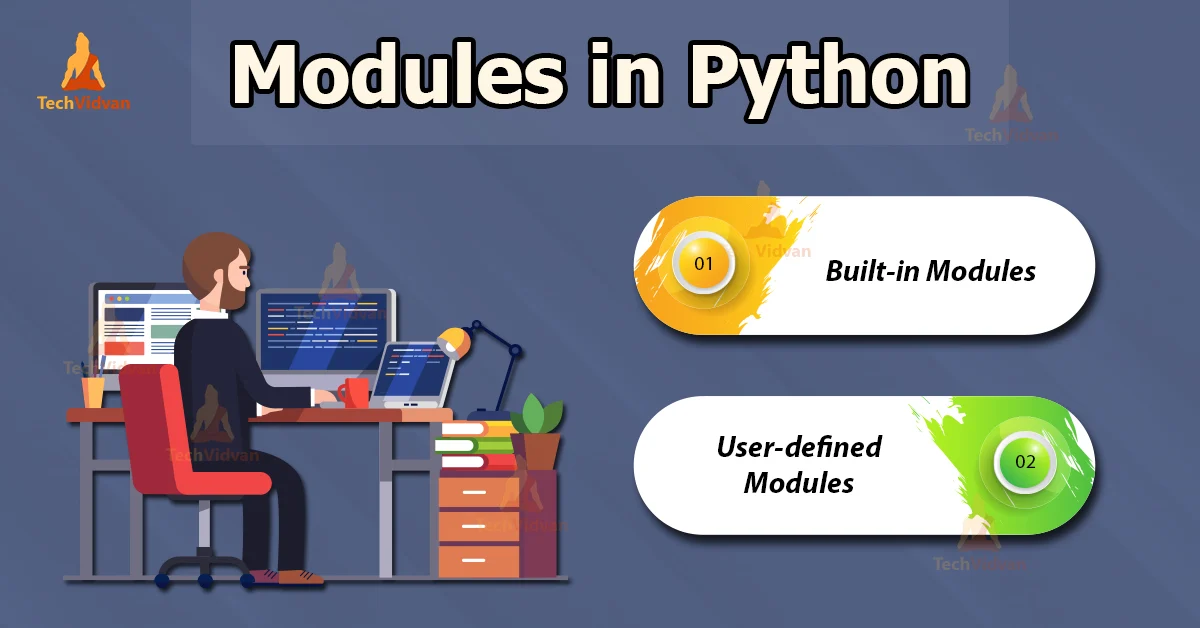
Understanding Python Modules
Generally and in programming thus Python, a module in Python is a file that contains Python code. It is a way to organize Python code so that it can be reused across multiple Python scripts or applications. Each module can contain a set of functions, classes, and global variables that can be accessed from any script that imports that module.
Here’s an example of a Python module:
# my_module.py
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def subtract(a, b):
return a – b
-
Importing Python Modules
To use the functions or classes defined in a module, you need to import the module. The import statement in Python is used to import a module.
Here’s an example of how to import the my_module module:
import my_module
result = my_module.add(1, 2)
print(result) # Output: 3
result = my_module.subtract(5, 3)
print(result) # Output: 2
-
Using
from ... import ...Syntax
You can also import specific functions or classes from a module using the from ... import ... syntax. This allows you to directly use the imported functions or classes without needing to use the module name as a prefix.
Here’s an example of how to import the add and subtract functions from the my_module module:
from my_module import add, subtract
result = add(1, 2)
print(result) # Output: 3
result = subtract(5, 3)
print(result) # Output: 2
-
Importing * (All) from a Module
If you want to import all the functions and classes defined in a module, you can use the from ... import * syntax.
Here’s an example of how to import all the functions and classes from the my_module module:
from my_module import *
result = add(1, 2)
print(result) # Output: 3
result = subtract(5, 3)
print(result) # Output: 2
Please note that importing all the functions and classes from a module can potentially cause naming conflicts and make your code harder to understand. It’s generally recommended to import only the specific functions or classes that you need.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.