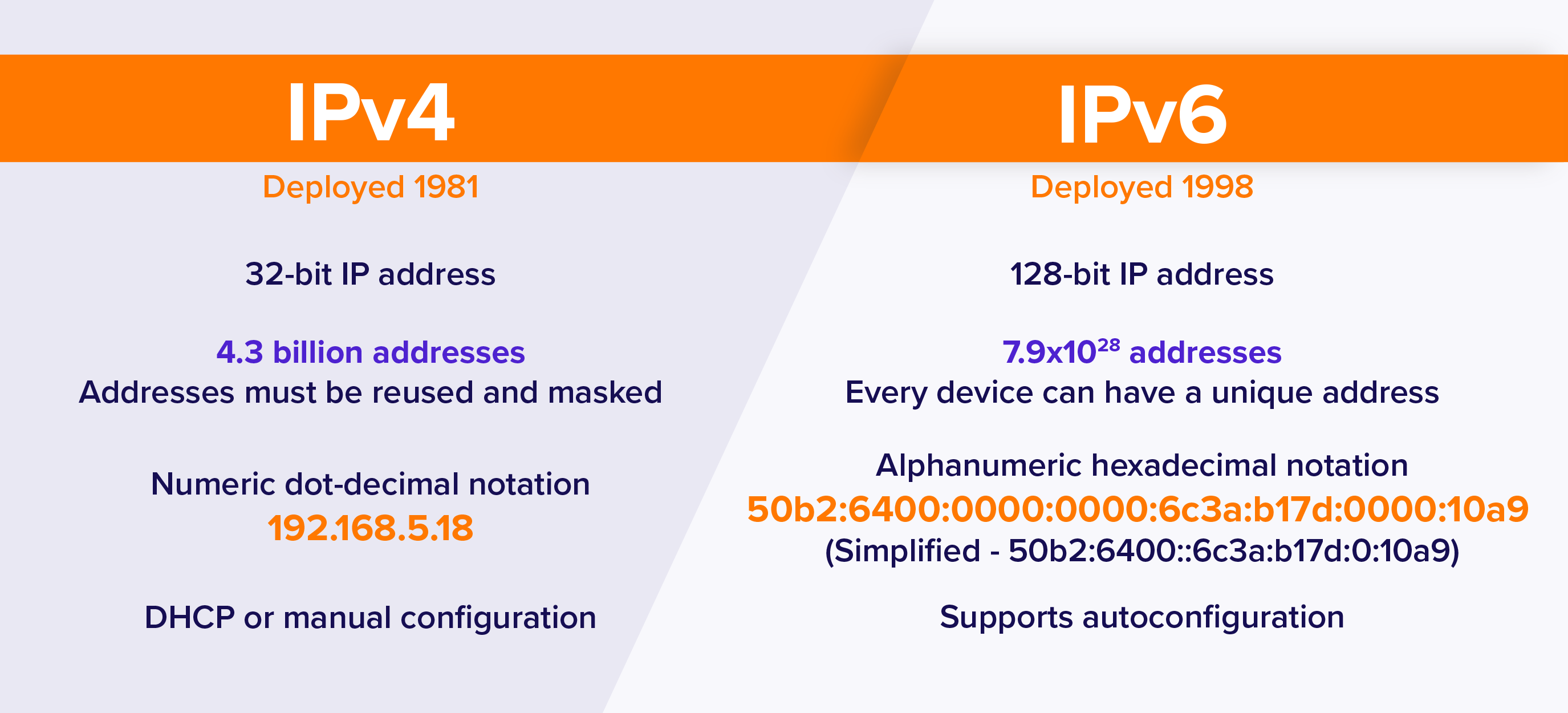
IPv4 and IPv6 are both types of Internet Protocol addresses that allow devices to communicate with each other on a network. IPv4 is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol and uses 32-bit addresses, which provides approximately 4 billion unique addresses. It represents addresses as four numbers separated by dots, for example, 172.16.254.1.
On the other hand, IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol and uses 128-bit addresses, which provides a much larger number of unique addresses, equivalent to 320 undecillion addresses. IPv6 represents addresses as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons, for example, 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
In summary, IPv4 and IPv6 are two different versions of Internet Protocol addresses, with IPv6 being more recent and providing a larger number of unique addresses than IPv4.
USES:
IP addresses have several uses in the internet protocol suite. Some of the primary uses include:
-
Identifying devices on a network: IP addresses are used to identify devices on a network. Each device on a network is assigned a unique IP address.
-
Routing data packets: When a device wants to send data to another device, it uses the IP address of the destination device to route the data packet. The IP address acts as a destination address for the data packet.
-
Load balancing: In a network with multiple servers, load balancing is used to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers. This helps to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed with traffic. IP addresses are used to identify the servers and distribute the traffic accordingly.
-
Security: IP addresses can be used to control access to specific devices or networks. By using IP address filtering, administrators can control which devices or networks can access specific resources or services.
-
Network management: IP addresses are used to monitor and manage network devices and traffic. Network administrators can use IP addresses to track the location of devices, monitor network traffic, and troubleshoot network issues.
-
Quality of Service (QoS): QoS is used to prioritize network traffic based on specific criteria. IP addresses can be used to identify specific types of traffic and prioritize them accordingly.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs are used to create secure, encrypted connections between devices over a network. IP addresses are used to identify the devices at each end of the VPN connection and establish the encrypted connection.
-
Network Address Translation (NAT): NAT is used to conserve IP addresses by allowing multiple devices to share a single IP address. IP addresses are used to identify the devices and route the data packets correctly.
Overall, IP addresses play a crucial role in the efficient operation and management of networks and the internet.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.