What is IP Addressing?
IP Addressing is a numerical labeling system that enables network-connected devices to communicate with each other. IP stands for Internet Protocol, which is a set of rules for transmitting and receiving data packets between computers.
Currently in use are IPv4 and IPv6, two versions of IP addressing.
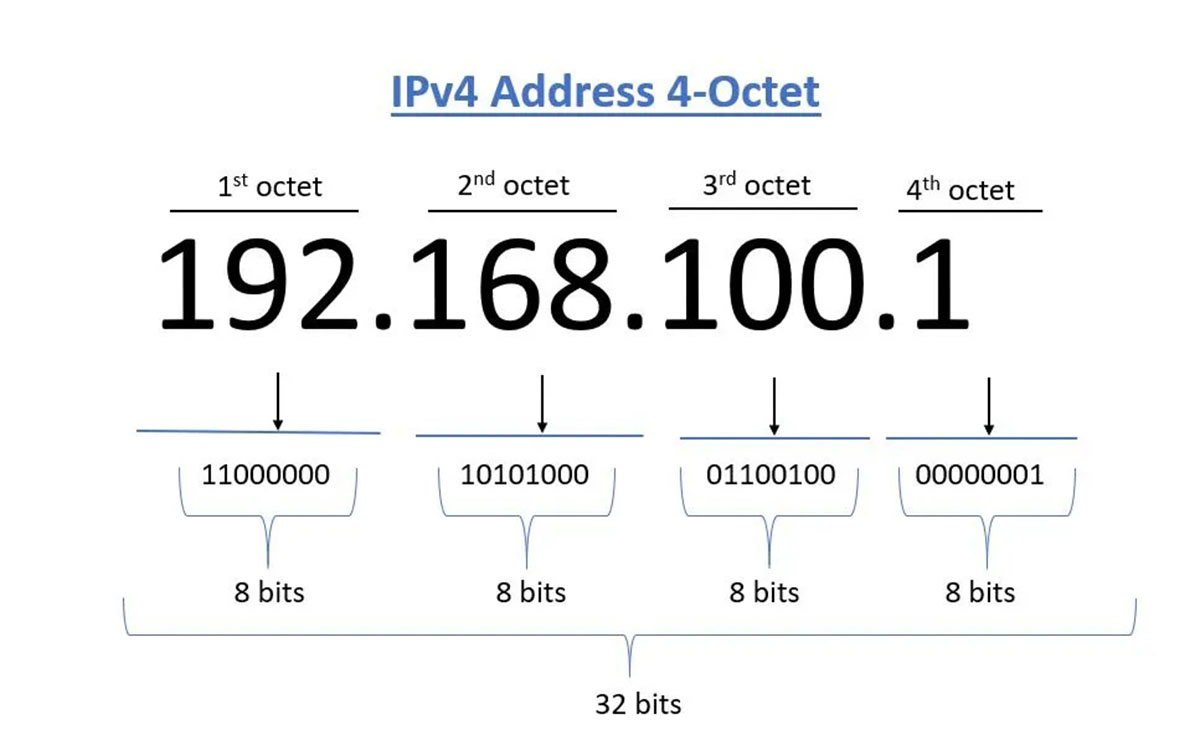
IPv4: In IPv4, IP addresses are 32-bit numbers that uniquely identify a device on the internet. These numbers are typically represented in a decimal format as four sets of numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
The current IPv4 addressing system is facing an exhaustion issue due to the limited number of IPv4 addresses available.
IPv6: In IPv6, IP addresses are 128-bit numbers that provide a virtually unlimited number of IP addresses. These numbers are typically represented in a hexadecimal format as eight sets of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
IPv6 was known to have been introduced to solve the exhaustion problem faced by IPv4.
However, in terms of networking, each device on an IP network has a unique IP address. These IP addresses are used to identify the source and destination of data packets, facilitating communication between devices.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.