DOS, an abbreviation for Disk Operating System, is a family of operating systems that allow computers to boot and run.
Developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s by the Microsoft Corporation, the original version of DOS was called MS-DOS, or simply DOS. This version of DOS was written in machine code, a low-level programming language where each command is represented by a single machine instruction.
Here are some examples of how DOS commands might be used:
The dir command thus creates a directory at the prompt.
The cd.. and cd command is to change, command or switch between directories or subdirectories
The copy and cut command is used to replicate files and directories
DEL – Deletes a file.
MD – Creates a new directory.
RD – Deletes a directory.
These are just a few basic examples, but DOS commands are more diverse and allow users to perform various tasks, such as formatting hard drives, managing printers, and controlling system settings. First, ensure that SQL Server is installed on your computer.
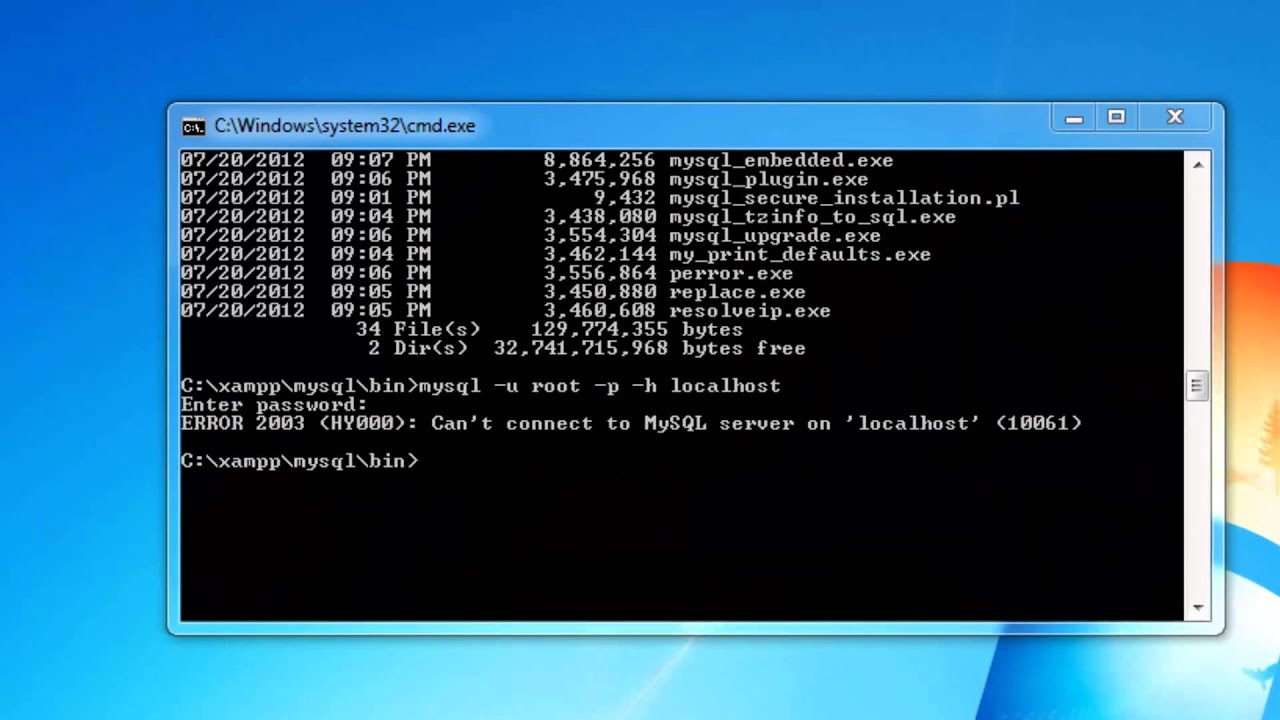
How to connect to a database using DOS
1. Open a Command Prompt (DOS) window.
2. In the DOS prompt, apply the following syntax:
that is: replace ServerName with the name of your SQL Server instance.
3. Replace UserName with your SQL Server login username.
4. Replace Password with your SQL Server login password.
Next is: Replace DatabaseName with the name of the database you prefer to connect to.
5. Press Enter to execute the command.
If you have successfully connected to the database, you will see the SQL Server command prompt: 1>.
To disconnect from the database, type the following command at the SQL Server command prompt:
Press Enter to execute the command. This will close the DOS window.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.