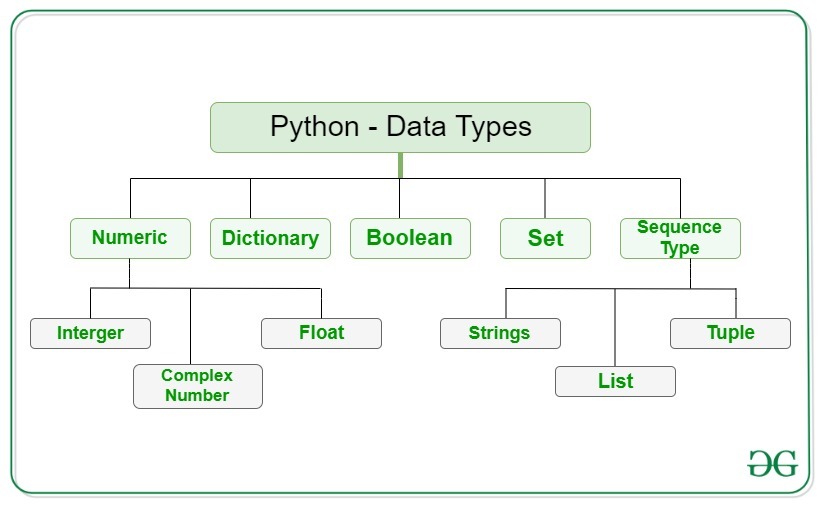
The following are data types in Python Programming Language.
Integer: The data type for whole numbers.
Example: a = 5
Float: The data type for real numbers, i.e., numbers with decimal points.
Example: b = 3.14
Complex: The data type for complex numbers, i.e., numbers of the form a + bj, where a and b are floats and j represents the square root of -1.
Example: c = 3 + 4j
String: The data type for sequences of characters, enclosed in single or double quotes.
Example: d = ‘Hello, World!’
Boolean: The data type for logical values, either True or False.
Example: e = True
None: A special constant in Python that represents the absence of a value or a null value.
Example: f = None
Outlines of Python operations and data structures:
Arithmetic operations such as the addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, floor division, modulus, and exponentiation.
String operations: concatenation, repetition, indexing, slicing, and various built-in methods.
List operations: indexing, slicing, various built-in methods like append(), extend(), etc.
Control structures: conditional statements (if-else) and loops (for and while).
Functions: reusable blocks of code that can be defined and called.
Data types: integers, floats, complex numbers, strings, booleans, and None.
These operations and data structures, among others, allow programmers to write efficient and flexible Python code.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.