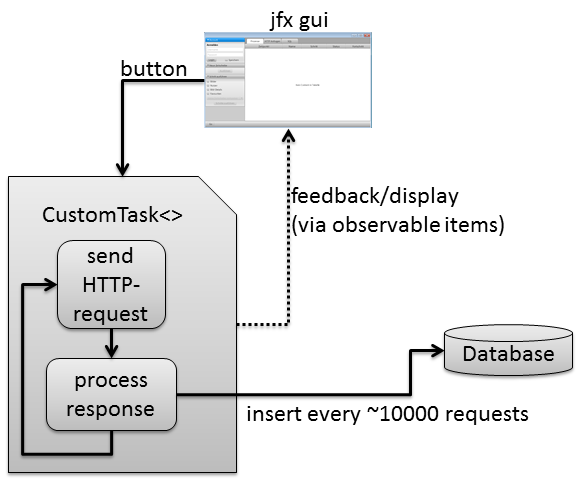
To create a thread pool in Python, we can use the `ThreadPoolExecutor` class from the `concurrent.futures` module. Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to use it:
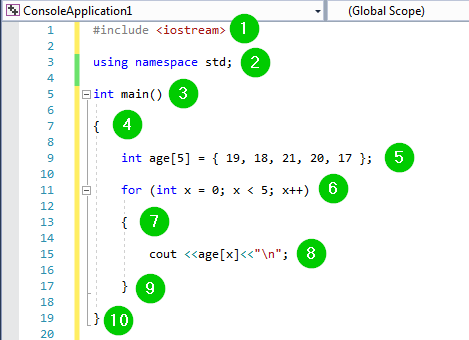
import requests
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def fetch_url(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response.text
urls = [‘https://www.google.com’, ‘https://www.yahoo.com’, ‘https://www.facebook.com’]
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
results = executor.map(fetch_url, urls)
for result in results:
print(result)
In this example, we define a function `fetch_url` that takes a URL as input and returns the response text. We then define a list of URLs to fetch.
We then create a `ThreadPoolExecutor` with a maximum of 5 workers. We use the `map` method of the executor to call the `fetch_url` function for each URL in the list.
Finally, we iterate over the results and print them out.
Note that the `ThreadPoolExecutor` class is a context manager, so we use it in a `with` block to ensure that the executor is properly closed when we’re done with it.
import requests
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def fetch_url(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response.text
urls = [‘https://www.google.com’, ‘https://www.yahoo.com’, ‘https://www.facebook.com’]
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
results = executor.map(fetch_url, urls)
for result in results:
print(result)
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.