Wireless networking has become increasingly popular over the past few decades, enabling devices to communicate with each other wirelessly over short or long distances. The three most common wireless networking technologies are Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and ZigBee.
Here’s a brief overview of each technology:
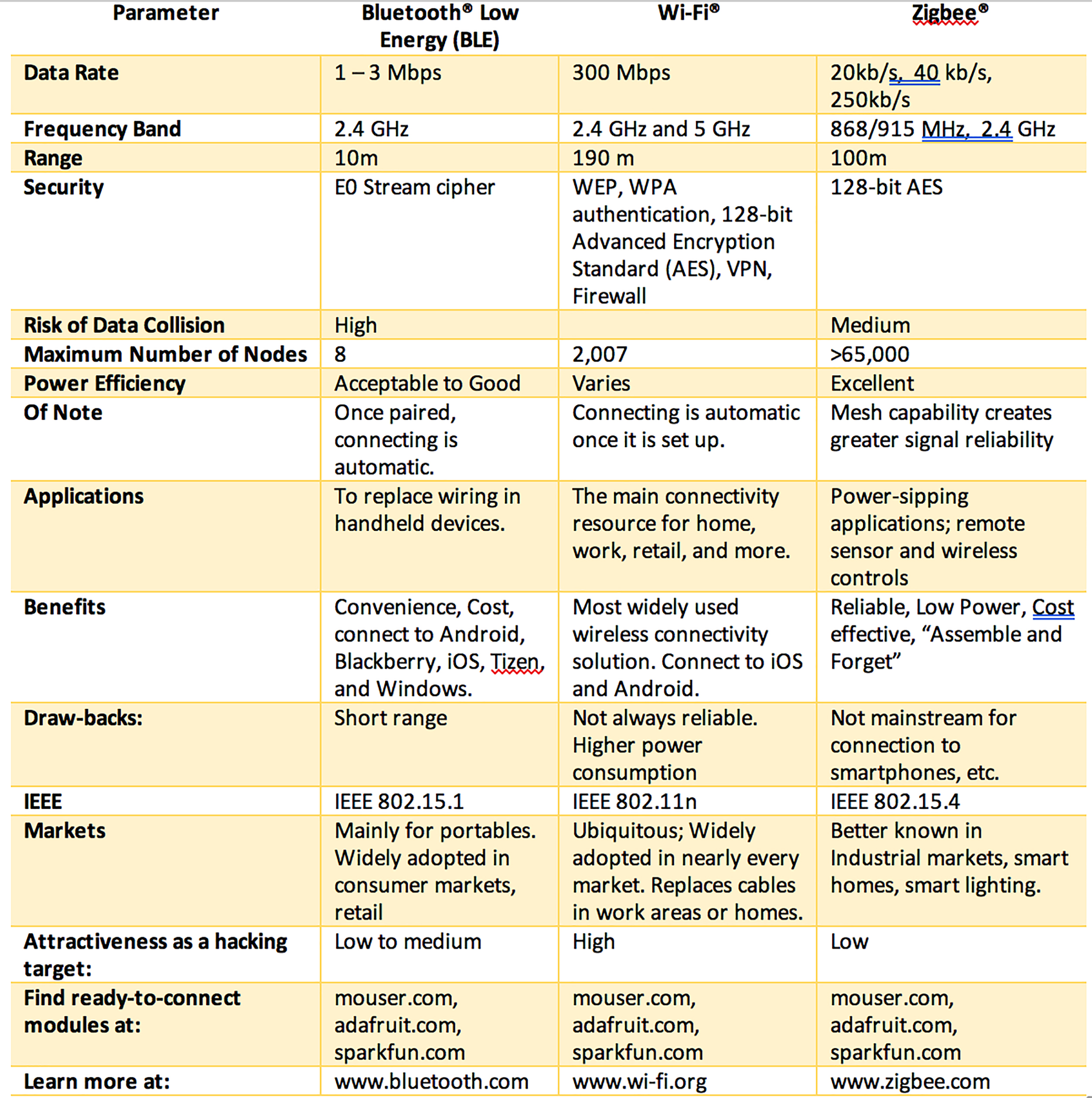
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to transmit and receive data over short distances. It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standards and can operate on various frequency bands, including 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. Wi-Fi is primarily used for internet access and local area networking (LAN), providing high data transfer rates and ranges of up to several hundred feet.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology that enables devices to communicate with each other over distances of up to about 30 feet. It is based on the IEEE 802.15.1 standard and uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Bluetooth is commonly used for wireless audio, data transfer, and device pairing, such as connecting a wireless headset to a smartphone.
- ZigBee: ZigBee is a low-power, low-data-rate wireless technology that is based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and provides ranges of up to several hundred feet. ZigBee is primarily used for wireless sensor networks and home automation applications, providing low power consumption and high reliability.
Each of these wireless networking technologies has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technology depends on the specific use case and requirements. Wi-Fi is ideal for high-speed internet access and local area networking; Bluetooth is well-suited for short-range device pairing and audio applications; and ZigBee is perfect for low-power, low-data-rate wireless sensor networks.
Related posts:
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.