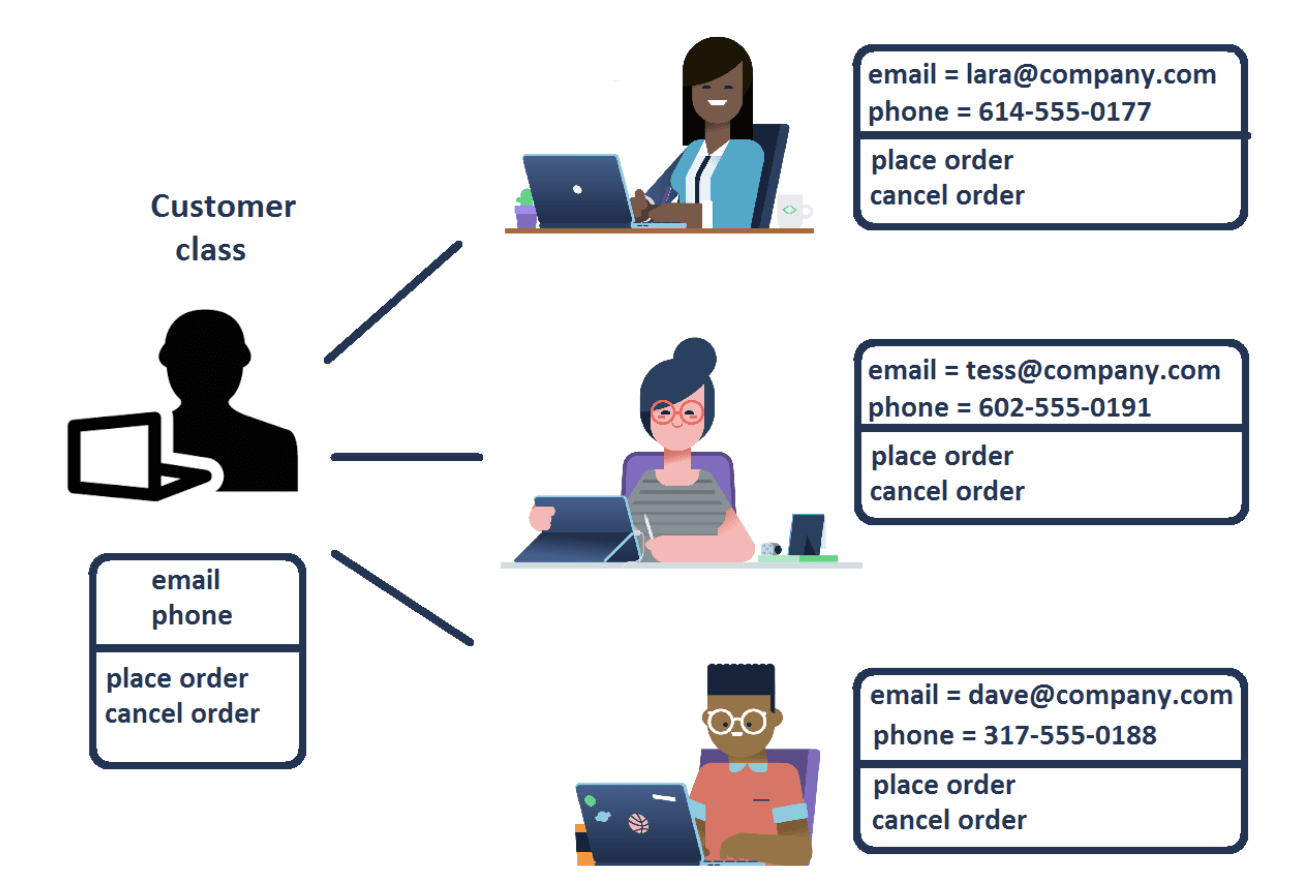
In Python, classes are a fundamental component of the language that enables you to create objects and define the behavior of these objects. In a way, classes are blueprints for creating objects.
When you create a class, you are essentially defining a new data type that can have its own methods (functions) and attributes (variables). Here’s an example of how you can define a class in Python:
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def introduce(self):
print(f”Hello, my name is {self.name} and I am {self.age} years old.”)
In this example, Person is a class that represents a person. The class has an __init__ method, which is a special method that is called when an object is created from the class. This method sets the attributes name and age for the object.
Theintroduce method is a regular method that prints an introduction message for the person.
To create an object from the Person class, you can use the following code:
person1 = Person(“Alice”, 30)
person1.introduce() # Output: Hello, my name is Alice and I am 30 years old.
In this example, we create an object person1 of the Person class. We then call the introduce method of person1 to print its introduction message.
It’s important to note that the syntax and concepts related to classes in Python can be complex and might take some time to fully understand and master. However, understanding classes is crucial for creating complex programs in Python, as they provide a way to encapsulate related data and functions.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.