In C++, strings and character arrays are used to store and manipulate sequences of characters, which are typically used to represent text.
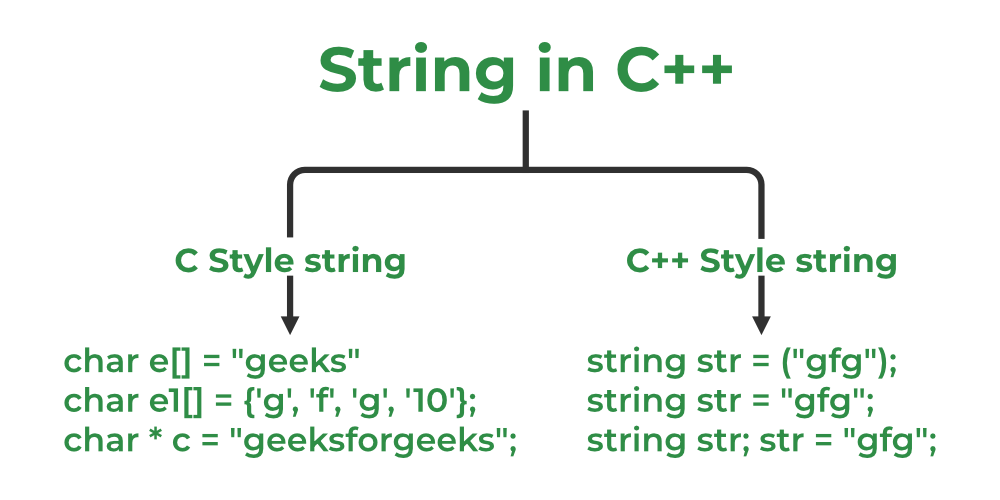
A string in C++ is a sequence of characters that is terminated by a null character (‘\0’). Strings can be declared as a fixed-size array of characters or as a variable-length object using the string class from the Standard Template Library (STL).
Here’s an example of declaring a string as a fixed-size array:
char greeting[10] = “Hello”;
In this example, the greeting array has a size of 10 characters, and it is initialized with the string “Hello“, which includes the null character at the end.
A character array, on the other hand, is simply an array of characters that is not necessarily terminated by a null character.
Find the below example of declaring a character array:
char name[5] = {‘J’, ‘o’, ‘n’, ‘ ‘, ‘D’};
In this example, the name array has a size of 5 characters, and it is initialized with the individual characters ‘J’, ‘o’, ‘n’, ‘ ‘, and ‘D’. Note that there is no null character at the end of this array, so it is not technically a string.
One important difference between strings and character arrays is that strings have built-in functions for manipulating and comparing strings, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp(). Character arrays, on the other hand, do not have these built-in functions and must be manipulated using pointer arithmetic or other low-level techniques.
In summary, strings and character arrays are both used to store and manipulate sequences of characters in C++, but strings have built-in functions for manipulation and comparison, while character arrays do not
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.