The most common and powerful Excel functions for beginners include:
SUM(): This function allows you to sum all the numbers in a specific range. For example, =SUM(A1:A10) would sum all the numbers in cells A1 through A10.
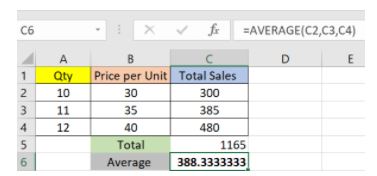
AVERAGE(): This function allows you to find the average of a set of numbers. For example, =AVERAGE(B1:B10) would calculate the average of all the numbers in cells B1 through B10.
MIN(): This function allows you to find the smallest number in a set of numbers. For example, =MIN(C1:C10) would find the smallest number in cells C1 through C10.
MAX(): This function allows you to find the largest number in a set of numbers. For example, =MAX(D1:D10) would find the largest number in cells D1 through D10.
IF(): This function allows you to apply conditional formatting in Excel. For example, =IF(E1>50, “High”, “Low”) would return “High” if the number in cell E1 is greater than 50 and “Low” otherwise.
VLOOKUP(): This function allows you to retrieve data from a different range or worksheet based on a specified lookup value. For example, =VLOOKUP(“John”, A1:B10, 2, FALSE) would retrieve the value in the second column (B) of the first worksheet (A1:B10), where the first column (A) matches “John.”.
HLOOKUP(): This function allows you to retrieve data from a different range or worksheet based on a specified lookup value. For example, =HLOOKUP(“Name”, A1:C1, 2, FALSE) would retrieve the value in the second row (B) of the first worksheet (A1:C1), where the first row (A) matches “Name”.
COUNT(): This function allows you to count the number of cells within a specific range that contain numeric values. For example, =COUNT(E1:E10) would count the number of numeric values in cells E1 through E10.
CONCATENATE(): This function allows you to merge multiple pieces of text into a single text string. For example, =CONCATENATE(“Hello, “, “John Doe!”) would merge “Hello, “, and “John Doe!” into a single text string.
LEFT(): This function allows you to extract a specified number of characters from the left side of a text string. For example, =LEFT(“John Doe”, 5) would extract the first five characters (“John”) from the text string “John Doe.”.
These are just a few examples of the many powerful Excel functions available. Familiarizing yourself with these functions can significantly improve your efficiency and effectiveness in Excel.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.