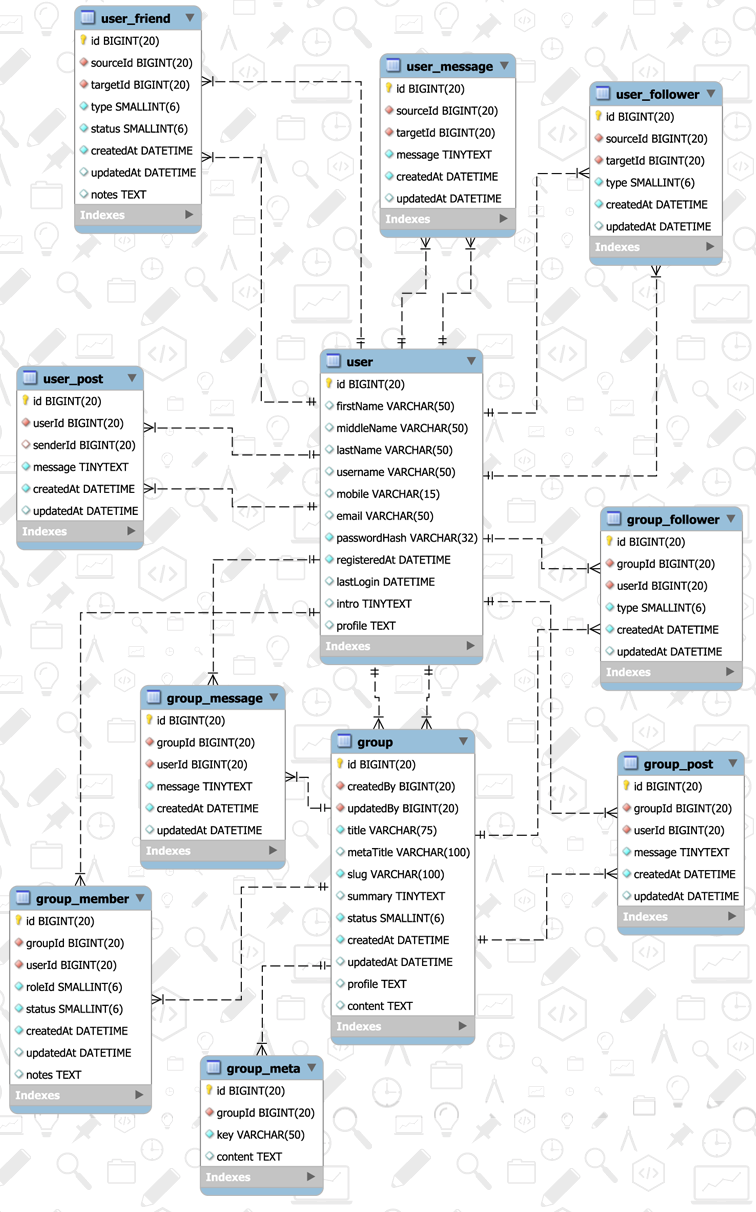
Users: This table will store all user-related information. Fields include user ID (unique), username, email, password, date of birth, profile picture, and bio.
Relationships: This table will store information about the connections between users. Fields include relationship ID (unique), user ID (of the person being connected to), friend’s user ID (of the person making the connection), and connection date.
Posts: This table will store all user-generated posts, including status updates, images, videos, and links. Fields include post ID (unique), user ID (of the person posting), content type (text, image, video, link), content, date posted, and any additional metadata (e.g., image caption, video title, link description).
Comments: This table will store all comments made on posts. Fields include comment ID (unique), user ID (of the person commenting), post ID (of the post being commented on), comment text, and comment date.
Likes: This table will store all “likes” made by users on posts. Fields include like ID (unique), user ID (of the person liking), post ID (of the post being liked), and like date.
To handle database growth and scalability, it is important to design a scalable schema. Indexing can be used to speed up query execution times.
NOTE:
To prevent data loss and maintain data integrity, implement proper backup and recovery procedures. Additionally, implementing appropriate security measures, such as encryption and user authentication, is crucial to protecting the data stored in the database.
By considering factors such as the scalability of the system, user privacy, and the overall efficiency of the system, a well-designed database schema can be implemented for a social networking site.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.