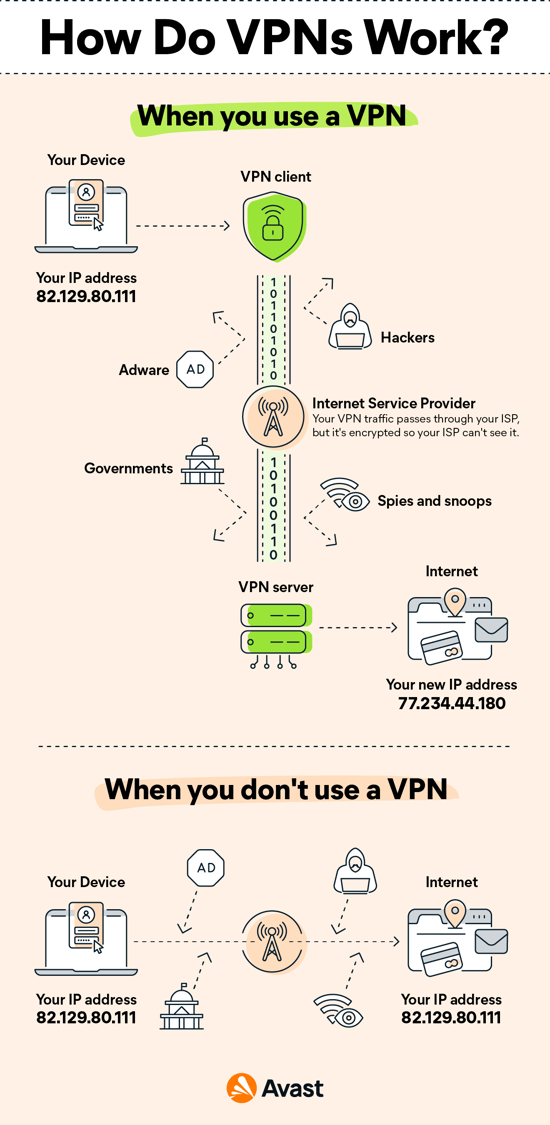
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a technology that creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and a VPN server.
What does it do?
Secures your online data: When you use a VPN, all of your internet data is encrypted. This ensures that no one, including your internet service provider (ISP), can monitor or access your data.
Provides a private online experience: When you connect to a VPN, your device obtains an IP address from the VPN server. Meanwhile, this gives the impression that you are accessing the internet from a different location for the entire phase.
Unblocks geo-restricted content: VPNs can change your IP address, allowing you to access geo-restricted content that may not be available in your region.
Enhances security on public Wi-Fi networks: When using a public Wi-Fi network, a VPN provides an extra layer of security by encrypting your data and protecting your online activity from prying eyes.
Why might I need one?
If you frequently use public Wi-Fi networks, a VPN can help protect your privacy and security by encrypting your data.
If you want to unblock geo-restricted content or access the internet securely while travelling, a VPN can be very useful.
If you work remotely or access work-related resources, a VPN can provide a secure and reliable connection to your company’s network.
If you want to maintain online privacy and anonymity, a VPN can help hide your real IP address.
It’s important to note that while a VPN can offer a high level of security and privacy, it does not provide absolute protection. VPN services can still be subject to government requests for user information, and they may have their own privacy policies.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.