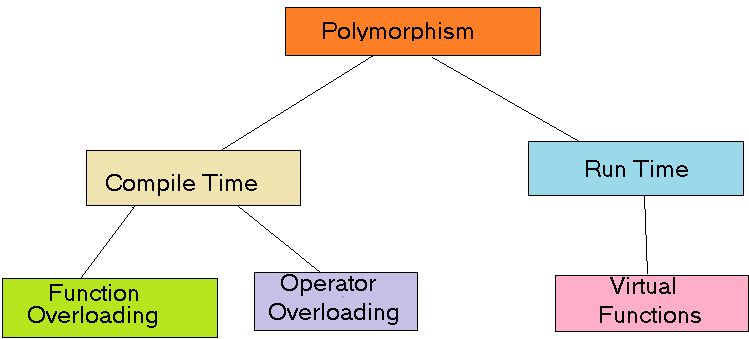
Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on different forms. Internationally and in the field of object-oriented programming, polymorphism on the other hand is verified and achieved through a method of overriding. This means that a subclass can define a different implementation of a method inherited from a superclass.
For example, consider the following Java code:
public class Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println(“Animal makes a sound.”);
}
}
public class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println(“Dog barks.”);
}
}
public class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println(“Cat meows.”);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Animal();
note to feed the system with the sound that is, for example, animal.makeSound(); // prints “Animal makes a sound.”
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.makeSound(); // prints “Dog barks.”
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.makeSound(); // prints “Cat meows.”
}
}
In this example, the `makeSound()` method is polymorphic. This means that it can be called on an object of any type that inherits from the `Animal` class, and the method will be executed differently depending on the type of object.
It is known that the terminology, Polymorphism is one of the strongest and also noted to be a powerful tool that has the ability to note and write more flexible and reusable code. It is also one of the key concepts in object-oriented programming.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.