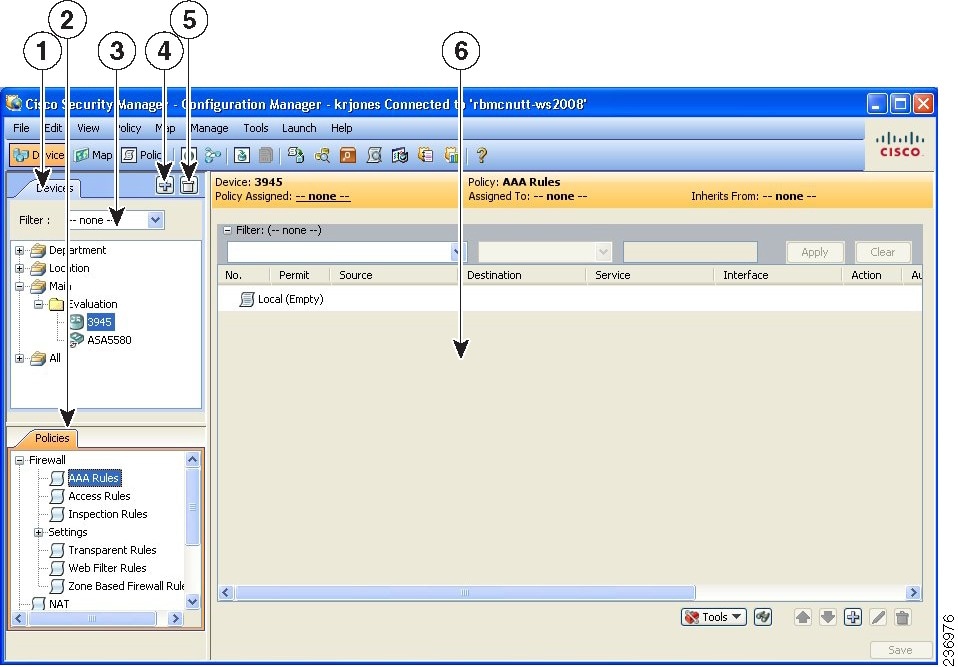
Server Management Studio (SMS) is a tool that allows users to manage their servers. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that makes it easy to perform common tasks such as creating and managing users, groups, and permissions; installing and configuring software; and monitoring system performance.
To set up server management software, follow these steps:
1. Choose the right software for your needs. There are many different server management software options available, each with its own unique features. Some of the most popular options include SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor, ManageEngine OpManager, Nagios XI, Zabbix, and Icinga 2. Consider the size of your network, the types of servers you have, and your budget when choosing a software solution.
2. Install the software. Once you have chosen a software solution, download and install it on your local computer.
3. Connect to your servers. Once the software is installed, you can connect to your servers using the GUI. The GUI will provide you with a number of features that allow you to perform common tasks such as creating and managing users, groups, and permissions; installing and configuring software; monitoring system performance; and troubleshooting problems.
4. Configure the software. Once you have connected to your servers, you will need to configure the software. This will typically involve specifying the IP addresses of your servers, setting up user accounts, and configuring the software’s monitoring and alerting features.
5. Start using the software. Once the software is configured, you can start using it to manage your servers. The software will provide you with a number of features that allow you to automate tasks, improve security, and troubleshoot problems.
Here are some commands and their meanings in server management software:
* **ls:** List the contents of a directory.
* **cd:** Change the current directory.
* **mkdir:** Create a new directory.
* **rm:** Remove a file or directory.
* **cp:** Copy a file or directory.
* **mv:** Move a file or directory.
* **chown:** Change the owner of a file or directory.
* **chmod:** This command is used to change the permissionor an authenticity of a file in the system.
* **su:** Switch to the root user.
* **exit:** Exit the current shell.
About Author
Discover more from SURFCLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.